Characterization of Nutritional and Bioactive Properties of Coffea canephora Pulp and Its Aqueous Extract Using Conventional and Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction
Item
-
Tittle
-
Characterization of Nutritional and Bioactive Properties of Coffea canephora Pulp and Its Aqueous Extract Using Conventional and Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction
-
Conference Acronym
-
IHSATEC 2025: 18th HASIB
-
DOI Number
-
doi.org/10.31098/HST25146
-
Conference Date
-
December 18, 2025
-
presented at
-
The International Halal Science and Technology Conference 2025 (IHSATEC): 18th Halal Science Industry and Business (HASIB)
-
Poster Author(S)
-
Muhammad Eriansyah Al Hakim
-
Conference Theme
-
IHSATEC 2025: 18th HASIB
-
Abstract
-
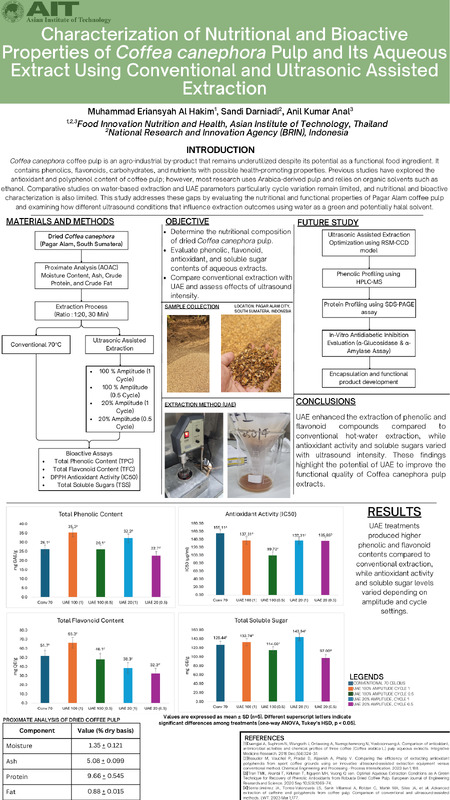
Background – Coffee pulp has been an agro-industrial waste that produces massively across coffee-producing countries, such as indonesia. Coffee pulp shows potential as a sustrainable functional food ingridient with health-promting properties. However, scientific data on its nutritional and biaoctive composition are remain limited, especially for region-specific coffea canephora materials.
Purpose – This study aims to evaluate the nutritional composition and functional properties of dried coffea canephora pulp and to characterize the bioactive properties through different two extraction methods and assess its effects of the ultrasound activity using water as solvent for halal and greener approaches.
Design/methodology/approach – Dried coffee pulp was collected from Pagar Alam, South Sumatra, and analyzed using standard AOAC procedures for moisture, ash, crude protein, crude fat, and total soluble sugars. Aqueous extracts were prepared using conventional extraction at 70°C and UAE at different amplitude and cycle settings. Total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, antioxidant activity (IC₅₀), and total soluble sugars were measured using spectrophotometric methods to evaluates the extraction performance and functional properties.
Findings – UAE has shown higher phenolic and flavonoid contents compared to the conventional method. Antioxidant activity also has different results between the extraction approaches, with UAE showing more stronger radical-scavenging power. Differences between UAE amplitudes and cycles is indicating that ultrasound intensity can influence the stability and solubility of compounds present in coffee pulp. Total soluble sugars also showing variationt across treatments, indicating difference solubilization efficiency during extractions.
Research limitations – This study strictly limited to coffea canephora coffee pulp from Pagar Alam City, South Sumatera, Indonesia and the solvent is focused on aqueous extraction and only basic bioactive analysis assays. Additional analysis such HPLC Phenolic profiling, antidiabetic enzymatic assays, or extraction optimization were not included. The findings are represents specific sample and may vary on coffee pulp variety, maturity, drying process, and processing conditions.
Originality/value – This study provides baseline scientific information on coffea canephora pulp from Pagar Alam City, It demonstrates how UAE can enhance the extraction of the bioactive compounds and supports the potential use of coffee pulp as a value-added ingredient for functional food applications. The findings contribute to efforts in utilizing coffee by-products within sustainable and circular bioeconomy frameworks.
-
Publisher Name
-
Yayasan Sinergi Riset dan Edukasi
-
Publication Date Online
-
December 18, 2025