Ensuring Halal Integrity and Food Safety in Sustainable Pesantren-Based SMEs: A Comprehensive HACCP and HGMP Approach
Item
-
Tittle
-
Ensuring Halal Integrity and Food Safety in Sustainable Pesantren-Based SMEs: A Comprehensive HACCP and HGMP Approach
-
Conference Acronym
-
IHSATEC 2024: 17th HASIB
-
DOI Number
-
https://doi.org/10.31098/HST24115
-
Conference Date
-
December 19-20, 2024
-
presented at
-
The International Halal Science and Technology Conference 2024 (IHSATEC): 17th Halal Science Industry and Business (HASIB)
-
Poster Author(S)
-
Galuh Tri Pambekti, Alya Mafaza, Atika Yahdiyani Ikhsani
-
Conference Theme
-
IHSATEC 2024: 17TH HASIB
-
Abstract
-
Abstract
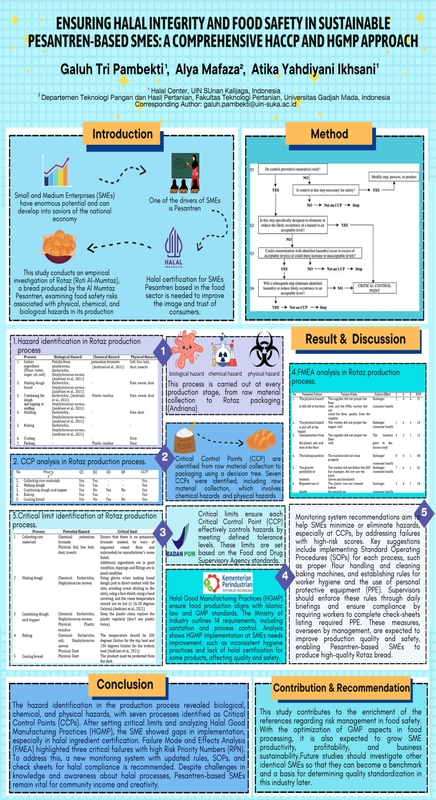
Background – The growing demand for halal-certified products, particularly in Indonesia, where Muslims form the majority, underscores the need for stringent food safety measures and halal integrity in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), especially those operating within pesantren (Islamic boarding schools)
Purpose – The purpose of this study was to examine the halal assurance and food safety practices of Rotaz, a bread product manufactured by Al Mumtaz Pesantren. As a pesantren-based SME, Rotaz faces various production risks, including physical, chemical, and biological hazards, which could potentially impact both halal integrity and food safety.
Design/methodology/approach – This study uses the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) and Halal Good Manufacturing Practices (HGMP) frameworks to analyze risks in the halal production process of Rotaz, alongside a Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) to identify and prioritize critical risks. This empirical research aims to pinpoint stages within the production process that require stricter monitoring and to propose a model for sustainable halal assurance and food safety compliance.
Findings – The findings reveal that Rotaz production involves multiple hazard points: three biological, five chemical, and seven physical hazards identified across various production stages. Critical Control Point (CCP) analysis identified five stages requiring close control to maintain product safety and quality. While HACCP established the necessary safety parameters, the HGMP analysis highlighted gaps in the implementation of best practices. The FMEA results identified three critical risks with a Risk Priority Number (RPN) exceeding the critical threshold, indicating the need for immediate action. Recommendations include enhanced standard operating procedures (SOPs), routine monitoring, and checklists to ensure consistent adherence to halal and safety protocols.
Research limitations – The limitation of this study lies in its focus on a single pesantren-based SME, which may limit generalizability. However, the findings provide valuable insights into the unique challenges faced by pesantren-based SMEs in maintaining halal standards and food safety.
Originality/value – The limitation of this study lies in its focus on a single pesantren-based SME, which may limit generalizability. However, the findings provide valuable insights into the unique challenges faced by pesantren-based SMEs in maintaining halal standards and food safety.
Keywords: SMEs Pesantren-based, halal good manufacturing practice (HGMP), HACCP, food safety, halal integrity
-
Publisher Name
-
Yayasan Sinergi Riset dan Edukasi
-
Publication Date Online
-
19-12-2024